- Forums
- :
- Core Technology - Magento 1.x
- :
- Magento 1.x Programming Questions
- :
- Php in CMS pages
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
Php in CMS pages
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Php in CMS pages
As far as I've already read, you cannot add php directly to a CMS page, but you can add it to a block then add that to the CMS page.
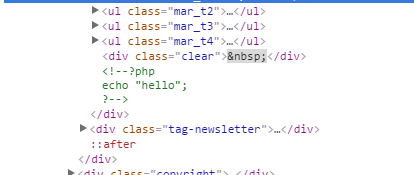
So why when adding it to a static block, would it comment out my code like so?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: Php in CMS pages
Is there an answer to this question? I am trying to the same, add php directly to the pages and have it render on the page. If you can't put it in a page or block, how does one go about adding custom PHP code to their site?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: Php in CMS pages
CMS Page PHP Restrictions – Most content management systems (CMS), like Magento, WordPress, or Joomla, do not allow PHP code directly in CMS pages. This restriction exists for security reasons, to prevent malicious code execution that could compromise your site.
Why Static Blocks Are Used – To include PHP functionality, you typically create a static block (sometimes called a widget or snippet) and then insert that block into the CMS page. This approach ensures that PHP executes in a controlled environment.
Automatic Commenting of PHP – If you try to paste PHP code directly into a static block, the CMS often comments it out automatically, for example:
<!--?php echo "Hello"; ?-->. This is done by the system’s HTML/PHP filters to prevent code execution in unsafe contexts.Filtering Settings – Many CMS have default filters that treat PHP as plain text inside blocks or pages. These filters may sanitize or escape PHP to prevent security risks.
Template Parsing – Static blocks are generally parsed by the CMS template engine. PHP will only run if the block is interpreted as a template file or allowed explicitly via settings.
Enabling PHP Execution – Some CMS platforms provide configuration options, modules , or extensions to enable PHP in static blocks safely. Without this, any PHP you add will be treated as a comment or string.
Food Menu Example – Suppose you want to display a dynamic food menu that fetches items from a database. If you insert the PHP directly in a CMS page, it will appear as text or be commented out.
Proper Approach – Instead, create a static block called Food Menu Block and insert your PHP code there to query the database for menu items. Then, use the CMS page to reference this block. Example directive in Magento:
{{block class="Vendor\Module\Block\FoodMenu" template="Vendor_Module::foodmenu.phtml"}}Custom Modules for PHP – Another secure approach is to create a custom module or template file that handles PHP execution for your food menu. Then, you can call this module from a CMS page without worrying about the CMS commenting out your code.
Why Blocks Are Safer – By using blocks, PHP code is isolated from direct user input, reducing the risk of code injection and ensuring that dynamic content like a food menu updates correctly.
Testing & Debugging – If your PHP is still commented out, check your CMS configuration:
Ensure PHP execution is allowed in blocks.
Clear cache if the CMS caches block output.
Verify that the syntax of your PHP code is correct.
Summary – Direct PHP in CMS pages is blocked for security. The solution is to place PHP in a static block or template. For example, a food menu can dynamically load items using PHP inside a block, then the block is added to the CMS page, ensuring the PHP executes safely without being commented out.