Optimizing storefronts with GraphQL in Magento 2
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Web APIs have been around for decades now, and as with any other technology, they are constantly evolving. When Magento was first released in 2007, SOAP and RPC were still the mainstream, so they became obvious choices for Magento’s machine-readable interface.
When Magento 2 was released in 2015, REST dominated in the web services space. Its main benefits over SOAP included developer friendliness and improved scalability due to statelessness and inherent cacheability. At the same time, Magento often integrates with legacy systems that may not support the newest available technologies. As a result, Magento 2 provides access to most of its service contracts via both REST and SOAP web APIs.
GraphQL is a newly emerged approach to web services that empowers development of optimized storefront experiences. We are not going to dive deep into GraphQL’s language specification, but more information can be found at graphql.org.
What are the benefits of GraphQL for storefront use cases?
-
You no longer need to perform multiple requests to fetch all data required on the page.
- You can specify only the fields you need rather than receiving all of them.
- GraphQL has excellent introspection and auto-completion capabilities for an improved developer experience.
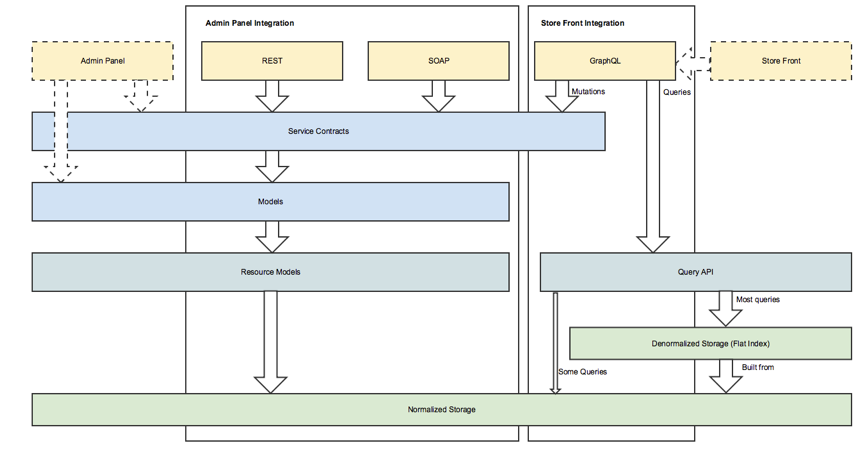
Magento decided to create a new set of APIs optimized for storefront pages. GraphQL makes a lot of sense for this scenario, because it can fetch all data needed in one request, and at the same time, it helps avoid sending excessive payloads over the network.
Technical vision for Magento web APIs shows that GraphQL can provide the highest value to storefront integrations. Eventually, all storefronts in Magento will fetch data using GraphQL.
GraphQL promises significant performance improvements over existing REST endpoints for read-only scenarios by leveraging a lighter infrastructure for read-only data on a storefront.
The first iteration of the GraphQL project includes support of products, categories, and customer queries. It is possible to extend existing queries or add support for new ones by customizing schemas and defining custom resolvers for fields. The Web API testing framework has been extended to allow you to test GraphQL queries.
The Products query is based on Magento collections. This means better performance compared to service contracts. A tradeoff is the need to customize query resolvers, in addition to existing service contracts customizations.
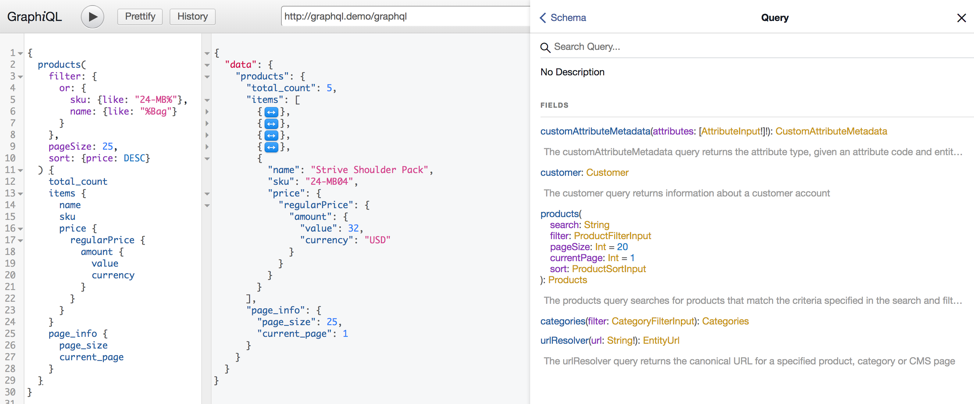
A number of developer tools support GraphQL. One of them is the GraphiQL browser extension, and it provides convenient way of querying data and viewing schema of any GraphQL service.
How to expose a new GraphQL query?
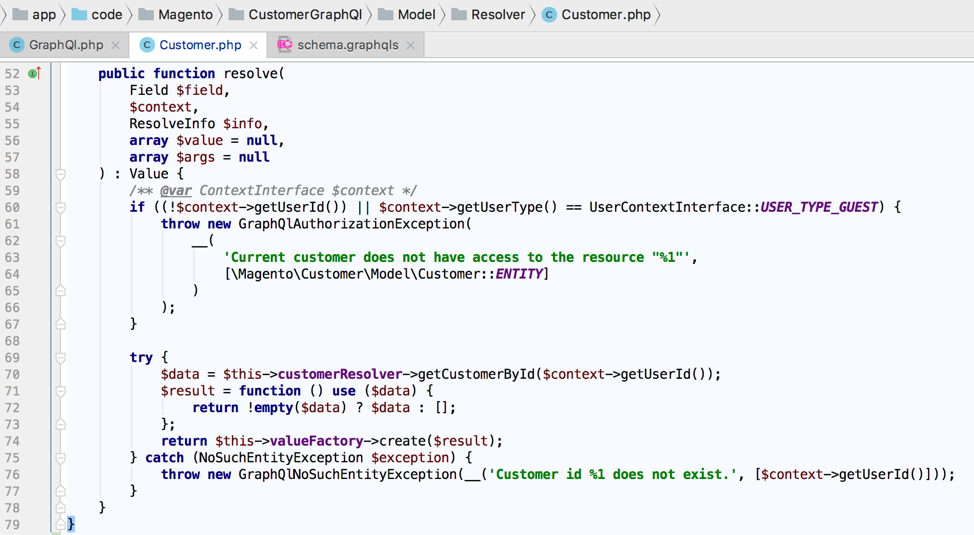
To expose a new GraphQL query or extend an existing one, extend the Magento 2 GraphQL schema and create a custom resolver. All resolvers must implement ResolverInterface.
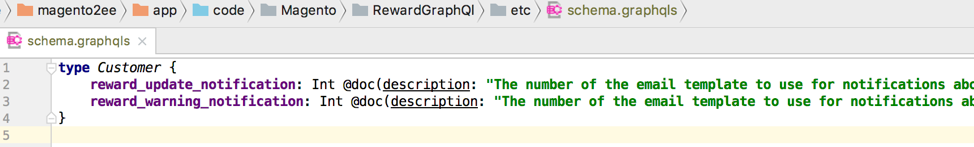
The following is an example of customer resolver.
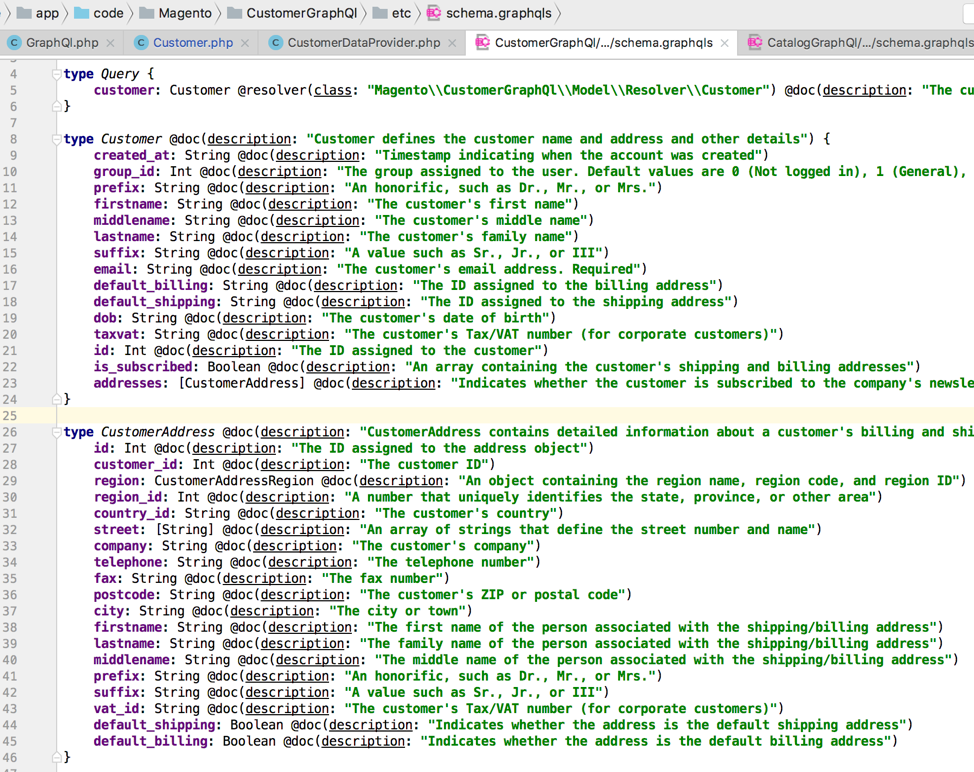
GraphQL SDL (Schema Definition Language) in Magento was extended to support modularity and avoid the need to use additional configuration files to declare resolvers.
You can extend a core Magento GraphQL type in a custom module without duplicating all the fields. The only requirement to make it work is a proper module loading sequence declared via etc/module.xml. The same extensibility principles apply to enumerations, interfaces, and inputs.
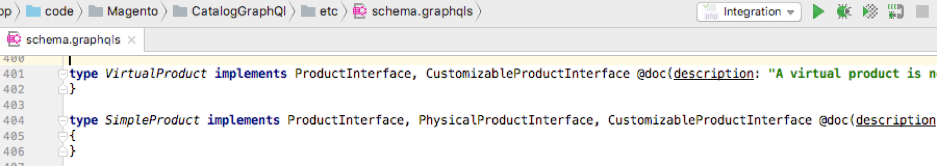
Another non-standard extension of Magento’s SDL is automatically copying fields from a GraphQL interface to its implementation. There is no need to duplicate all fields in the concrete type if they are declared in the interface. They will be automatically added to the merged Magento GraphQL schema. In the following example, VirtualProduct type gets all fields from ProductInterface and CustomizableProductInterface added to the resulting GraphQL schema.
For more information on GraphQL SDL, feel free to check out Graphcool’s blog.
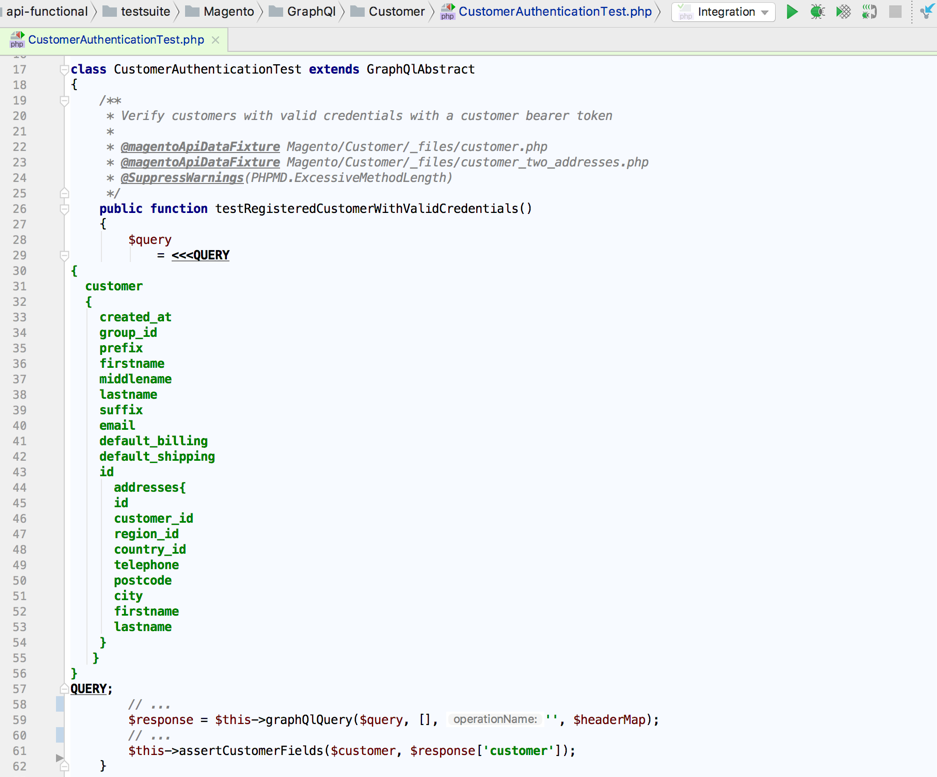
GraphQL queries can be tested using the specialized web API functional tests.
Just create a request in GraphiQL, and use it in a test case that inherits from GraphQlAbstract. The response will be automatically decoded and can be used for assertions.
You can already start playing with existing queries or define new ones using the code from the 2.3-develop branch.
How to contribute to the Magento 2 GraphQL project
The GraphQL community project was started to improve collaboration between the core team and community members who want to participate in the future of Magento web APIs. We have opened the GraphQL backlog so that community members can contribute to the next phase of the GraphQL project.
The Core Magento team is focusing on several areas:
- Integrating the early implementation of PWA to consume GraphQL data
- GraphQL mutations support
- Improved performance by introducing the read-only persistence module
We are looking for Community help with the following:
- Server-side caching for GraphQL queries. This might be tricky because of flexibility requirements. There are virtually an infinite number of unique queries that could be constructed with GraphQL
- Improving existing queries. For example, return 'Available sort options' for product listing
- Additional coverage for checkout, payment, shipping methods, orders, and customer accounts, for example
Community members have already contributed:
The true power of Magento is in its community, and if each of us contribute a bit, we all gain a lot. Your contributions can be the form of new feature, a bug fix, an issue report, or even a comment on Slack.
We have nice bounties for the Solution Partners as a part of our Contribution Program and moreover, we try to make improving the product a fulfilling experience for all users.
Head on over to the project link above and check out our GraphQL wiki to see how you can help!
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.